Briefly describe the following:
$(a)$ Transcription
$(b)$ Polymorphism
$(c)$ Translation
$(d)$ Bioinformatics
Briefly describe the following:
$(a)$ Transcription
$(b)$ Polymorphism
$(c)$ Translation
$(d)$ Bioinformatics
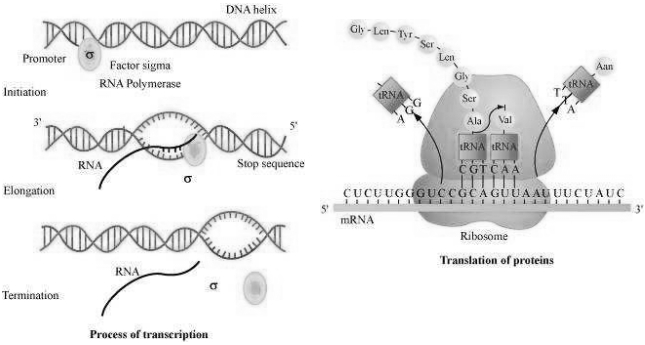
$(a)$ Transcription Transcription is the process of synthesis of $RNA$ from $DNA$ template. A segment of $DNA$ gets copied into $mRNA$ during the process. The process of transcription starts at the promoter region of the template $DNA$ and terminates at the terminator region. The segment of $DNA$ between these two regions is known as transcription unit. The transcription requires $RNA$ polymerase enzyme, a $DNA$ template, four types of ribonucleotides, and certain cofactors such as $\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$. T
he three important events that occur during the process of transcription are as follows.
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
The $DNA-$ dependent $RNA$ polymerase and certain initiation factors ( $\sigma$ ) bind at the double stranded $DNA$ at the promoter region of the template strand and initiate the process of transcription. $RNA$ polymerase moves along the $DNA$ and leads to the unwinding of $DNA$ duplex into two separate strands. Then, one of the strands, called sense strand, acts as template for $mRNA$ synthesis. The enzyme, $RNA$ polymerase, utilizes nucleoside triphosphates $(dNTPs)$ as raw material and polymerizes them to form $mRNA$ according to the complementary bases present on the template $DNA$. This process of opening of helix and elongation of polynucleotide chain continues until the enzyme reaches the terminator region. As $RNA$ polymerase reaches the terminator region, the newly synthesized $mRNA$ transcripted along with enzyme is released. Another factor called terminator factor ( $\rho$ ) is required for the termination of the transcription. (figure)
$(b)$ Polymorphism Polymorphism is a form of genetic variation in which distinct nucleotide sequence can exist at a particular site in a $DNA$ molecule. This heritable mutation is observed at a high frequency in a population. It arises due to mutation either in somatic cell or in the germ cells. The germ cell mutation can be transmitted from parents to their offsprings. This results in accumulation of various mutations in a population, leading to variation and polymorphism in the population. This plays a very important role in the process of evolution and speciation.
$(c) $ Translation Translation is the process of polymerizing amino acid to form a polypeptide chain. The triplet sequence of base pairs in $mRNA$ defines the order and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. The process of translation involves three steps.
Initiation
Elongation
Termination
During the initiation of the translation, $tRNA$ gets charged when the amino acid binds to it using $ATP$. The start (initiation) codon $(AUG)$ present on $mRNA$ is recognized only by the charged $tRNA$. The ribosome acts as an actual site for the process of translation and contains two separate sites in a large subunit for the attachment of subsequent amino acids. The small subunit of ribosome binds to $mRNA$ at the initiation codon $(AUG)$ followed by the large subunit. Then, it initiates the process of translation. During the elongation process, the ribosome moves one codon downstream along with $mRNA$ so as to leave the space for binding of another charged $tRNA$. The amino acid brought by $tRNA$ gets linked with the previous amino acid through a peptide bond and this process continues resulting in the formation of a polypeptide chain. When the ribosome reaches one or more $STOP$ codon $(VAA, UAG,$ and $UGA)$, the process of translation gets terminated. The polypeptide chain is released and the ribosomes get detached from $mRNA$. (figure)
$(d)$ Bioinformatics Bioinformatics is the application of computational and statistical techniques to the field of molecular biology. It solves the practical problems arising from the management and analysis of biological data. The field of bioinformatics developed after the completion of human genome project $(HGP)$. This is because enormous amount of data has been generated during the process of $HGP$ that has to be managed and stored for easy access and interpretation for future use by various scientists. Hence, bioinformatics involves the creation of biological databases that store the vast information of biology.
It develops certain tools for easy and efficient access to the information and its utilization. Bioinformatics has developed new algorithms and statistical methods to find out the relationship between the data, to predict protein structure and their functions, and to cluster the protein sequences into their related families.
Similar Questions
Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs
- [AIPMT 2005]
Full Forms :
$1.$ $\rm {DNA}$
$2.$ $\rm {RNA}$
$3.$ $\rm {hnRNA}$
$4.$ $\rm {UTR}$
Full Forms :
$1.$ $\rm {DNA}$
$2.$ $\rm {RNA}$
$3.$ $\rm {hnRNA}$
$4.$ $\rm {UTR}$
Give scientific reasons : It is essential that $ tRNA$ binds to both amino acids and $mRNA$ codon during
protein synthesis.
Give scientific reasons : It is essential that $ tRNA$ binds to both amino acids and $mRNA$ codon during
protein synthesis.
Read the following statements:
$A.$ Variation at genetic level arises due to mutations.
$B.$ Technique of $DNA$ fingerprinting was initially developed by Alec Jeffreys
Read the following statements:
$A.$ Variation at genetic level arises due to mutations.
$B.$ Technique of $DNA$ fingerprinting was initially developed by Alec Jeffreys
During in vitro synthesis of $DNA$, a researcher used $2',\,3'$ -dideoxy cytidine triphosphate as raw nucleotide in place of $2'-$ deoxy cytidine. What would be the consequence ?
During in vitro synthesis of $DNA$, a researcher used $2',\,3'$ -dideoxy cytidine triphosphate as raw nucleotide in place of $2'-$ deoxy cytidine. What would be the consequence ?


