Two wires of the same material (Young's modulus $Y$ ) and same length $L$ but radii $R$ and $2R$ respectively are joined end to end and a weight $W$ is suspended from the combination as shown in the figure. The elastic potential energy in the system is
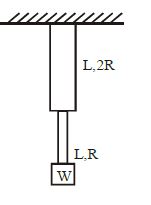
Two wires of the same material (Young's modulus $Y$ ) and same length $L$ but radii $R$ and $2R$ respectively are joined end to end and a weight $W$ is suspended from the combination as shown in the figure. The elastic potential energy in the system is

- A
$\frac{{3{W^2}L}}{{4\pi {R^2}Y}}$
- B
$\frac{{3{W^2}L}}{{8\pi {R^2}Y}}$
- C
$\frac{{5{W^2}L}}{{8\pi {R^2}Y}}$
- D
$\frac{{{W^2}L}}{{\pi {R^2}Y}}$
Similar Questions
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which more work will have to be done ?
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which more work will have to be done ?
The elastic behaviour of material for linear streass and linear strain, is shown in the figure. The energy density for a linear strain of $5 \times 10^{-4}$ is $\dots \; kJ / m ^{3}$. Assume that material is elastic upto the linear strain of $5 \times 10^{-4}$.
The elastic behaviour of material for linear streass and linear strain, is shown in the figure. The energy density for a linear strain of $5 \times 10^{-4}$ is $\dots \; kJ / m ^{3}$. Assume that material is elastic upto the linear strain of $5 \times 10^{-4}$.
- [JEE MAIN 2022]
A wire of length $L$ and cross-sectional area $A$ is made of a material of Young's modulus $Y.$ It is stretched by an amount $x$. The work done is
A wire of length $L$ and cross-sectional area $A$ is made of a material of Young's modulus $Y.$ It is stretched by an amount $x$. The work done is
The work done in increasing the length of a $1$ $metre$ long wire of cross-section area $1\, mm^2$ through $1\, mm$ will be ....... $J$ $(Y = 2\times10^{11}\, Nm^{-2})$
The work done in increasing the length of a $1$ $metre$ long wire of cross-section area $1\, mm^2$ through $1\, mm$ will be ....... $J$ $(Y = 2\times10^{11}\, Nm^{-2})$
If $x$ longitudinal strain is produced in a wire of Young's modulus $y,$ then energy stored in the material of the wire per unit volume is
If $x$ longitudinal strain is produced in a wire of Young's modulus $y,$ then energy stored in the material of the wire per unit volume is
- [AIIMS 2001]
